GMAT 750 Level Data Sufficiency Question 33
Coordinate Geometry | Quadratic Equations
The given question is a challenging GMAT 750 level data sufficiency question. This question tests concepts in Quadratic Equations and Coordinate Geometry.
GMAT Data Sufficiency | Directions | Click Here ▼
This data sufficiency problem consists of a question and two statements, labeled (1) and (2), in which certain data are given. You have to decide whether the data given in the statements are sufficient for answering the question. Using the data given in the statements, plus your knowledge of mathematics and everyday facts (such as the number of days in a leap year or the meaning of the word counterclockwise), you must indicate whether -
- Statement (1) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (2) alone is not sufficient to answer the question asked.
- Statement (2) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (1) alone is not sufficient to answer the question asked.
- BOTH statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are sufficient to answer the question asked, but NEITHER statement ALONE is sufficient to answer the question asked.
- EACH statement ALONE is sufficient to answer the question asked.
- Statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are NOT sufficient to answer the question asked, and additional data specific to the problem are needed.
Numbers
All numbers used are real numbers.
Figures
A figure accompanying a data sufficiency question will conform to the information given in the question but will not necessarily conform to the additional information given in statements (1) and (2)
Lines shown as straight can be assumed to be straight and lines that appear jagged can also be assumed to be straight
You may assume that the positions of points, angles, regions, etc. exist in the order shown and that angle measures are greater than zero.
All figures lie in a plane unless otherwise indicated.
Note
In data sufficiency problems that ask for the value of a quantity, the data given in the statement are sufficient only when it is possible to determine exactly one numerical value for the quantity.
Question 33: If y = (x - p)(x - q), is the sum of integers p and q positive?
Statement 1: The curve cuts the y-axis at -20.
Statement 2: Minimum value of y is -36.
Get to 705+ in the GMAT
Online GMAT Course
@ INR 10,000 + GST
Video Explanation
GMAT Live Online Classes
Starts Sat, Mar 07, 2026
Explanatory Answer | GMAT Algebra & Geometry Data Sufficiency Q33
Step 1: Decode the Question Stem and Get Clarity
Q1. What kind of an answer will the question fetch?
An "Is" question will fetch a definite "Yes" or a "No" as the answer.
The data provided in the statements will be considered sufficient if the question is answered with a conclusive Yes or a conclusive No.
Q2. What is the concept?
y = (x - p)(x - q) is a quadratic equation, whose roots are p and q - the points where the parabola cuts the x axis.
Step 2: Evaluate Statement 1 ALONE
Statement 1: The curve cuts the Y-axis at -20.
(0, -20) is a point on the curve. The point will satisfy y = (x - p)(x - q)
-20 = (0 - p)(0 - q)
pq = -20
Approach: Counter example
Example: p = 10, q = -2; pq = -20
p + q = 10 + (-2) = 8
Answer to the question is YES.
Counter Example: p = -10, q = 2; pq = -20
p + q = -10 + 2 = -8
Answer to the question is NO.
Counter Example exists.
We are not able to answer the question with a DEFNITE Yes or No.
Hence, statement 1 alone is not sufficient.
Eliminate answer option A and D.
Step 3: Evaluate Statement 2 ALONE
Statement 2: Minimum value of y is -36.
We know that y = (x - p) (x - q), where p and q are the roots of the equation.
Approach: Counter example
Example: Both p and q are positive for ymin = -36
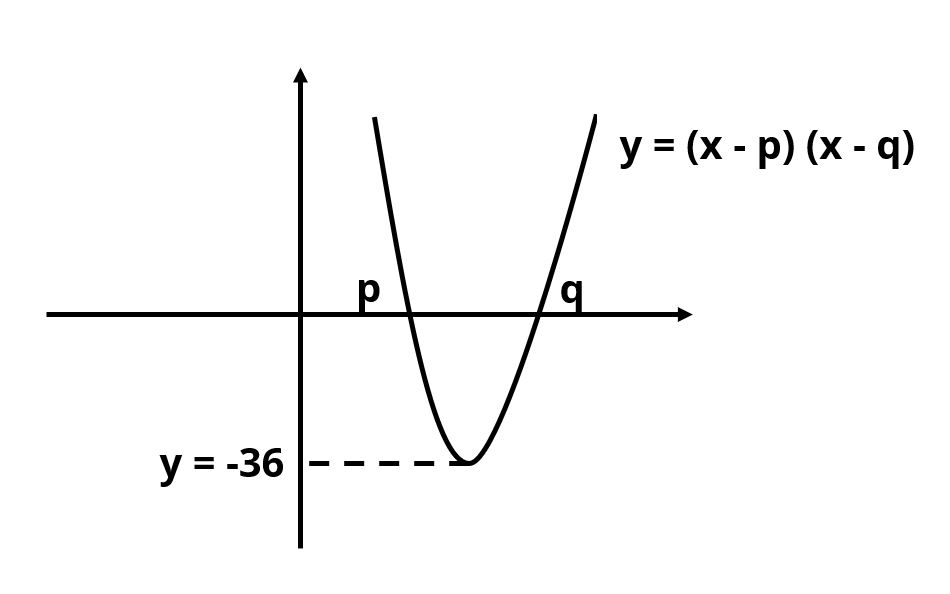
Now, the sum of p and q is positive.
Answer to the question is YES.
Counter Example: Both p and q are negative for ymin = -36
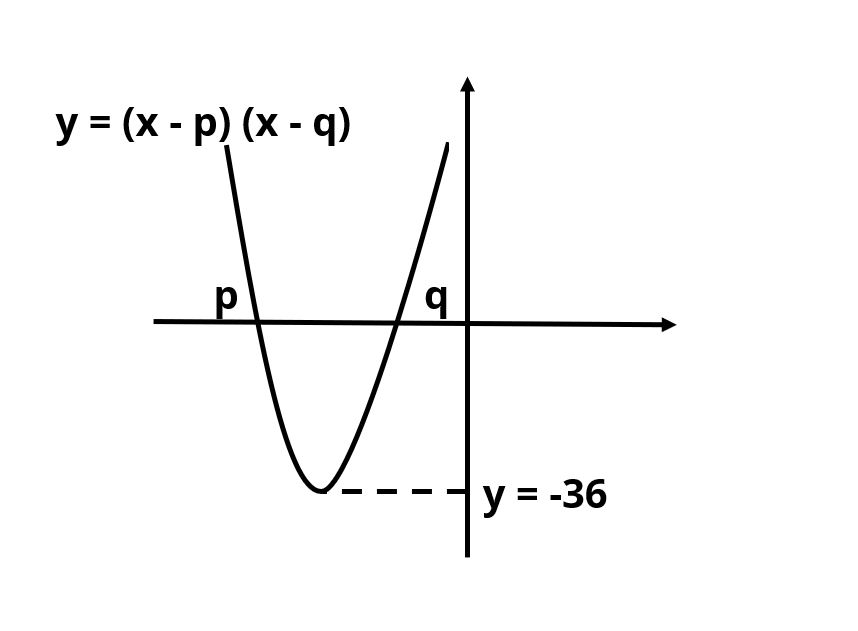
Now, the sum of p and q is negative.
Answer to the question is NO.
Counter Example exists.
We are not able to answer the question with a DEFNITE Yes or No.
Hence, statement 2 alone is not sufficient.
Eliminate answer option B.
Step 4: Evaluate Statements TOGETHER
Statements: From Statement 1: The curve cuts the Y-axis at -20.
From Statement 2: Minimum value of y is -36.
From the statements: pq = -20 and ymin = -36
In a parabola, the minimum value of y happens when x = \\frac{(r_1 + r_2)}{2}), where r1 and r2 are the roots of the equation.
| P | Q | x = \\frac{\text{(p + q)}}{\text{2}}) |
|---|---|---|
| -20 | 1 | \\frac{-19}{2}) |
| 20 | -1 | \\frac{-19}{2}) |
| -10 | 2 | \\frac{-8}{2}) = -4 |
| 10 | -2 | \\frac{8}{2}) = -4 |
| 5 | -4 | \\frac{1}{2}) |
| -5 | 4 | \\frac{-1}{2}) |
Example: p = -10, q = 2
y = (x + 10)(x – 2) ....(1)
y will be minimum when x = \\frac{\text{(p + q)}}{\text{2}}) = \\frac{\text{(−10 + 2)}}{\text{2}}) = -4
Substitute x = -4 in equation (1)
y = (-4 + 10)(-4 - 2) = 6 × -6 = -36
Now, p + q = -10 + 2 = -8
Answer to the question is NO.
Counter Example:p = 10, q = -2
y = (x - 10) (x + 2) ....(2)
y will be minimum when x = \\frac{\text{(p + q)}}{\text{2}}) = \\frac{\text{(10 - 2)}}{\text{2}}) = 4
Substitute x = 4 in equation (2) y = (4 - 10)(4 + 2) = -6 × 6 = -36
Now, p + q = 10 – 2 = 8
Answer to the question is YES.
Despite combining both the statements, we are not able to answer the question with a definite Yes or No.
Statement TOGETHER are NOT sufficient.
Eliminate answer option C.
Choice E is the correct answer.
GMAT Hard Math Videos On YouTube
GMAT Sample Questions | Topicwise GMAT Questions
Copyrights © 2016 - 26 All Rights Reserved by Wizako.com - An Ascent Education Initiative.
Privacy Policy | Terms & Conditions
GMAT® is a registered trademark of the Graduate Management Admission Council (GMAC). This website is not endorsed or approved by GMAC.
GRE® is a registered trademarks of Educational Testing Service (ETS). This website is not endorsed or approved by ETS.
SAT® is a registered trademark of the College Board, which was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse this product.
How to reach Wizako?
Mobile: (91) 95000 48484
WhatsApp: WhatsApp Now
Email: [email protected]
Leave A Message
